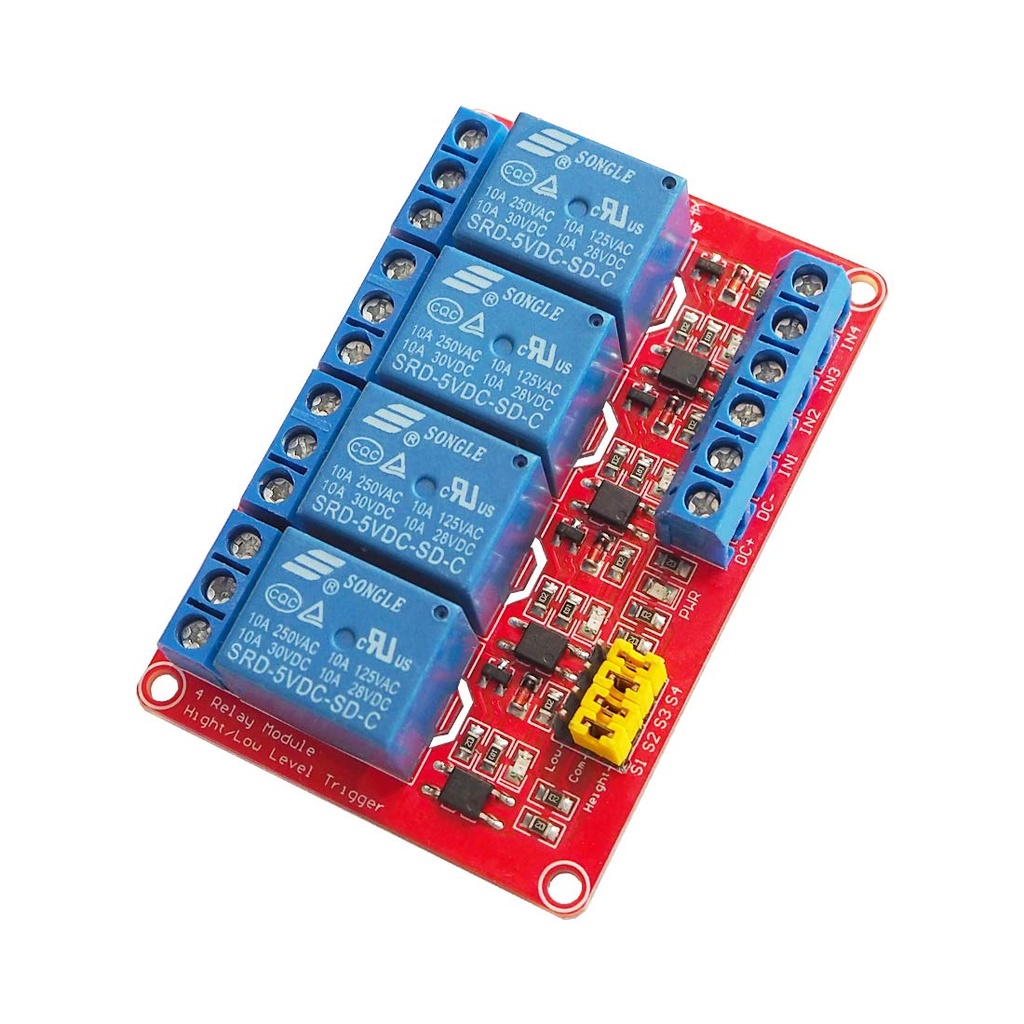
Features:
- Optocoupler Isolation: Reduces distortion and improves signal reliability.
- Dual Contact Design: Each relay provides Normally Closed (NC) and Normally Open (NO) contacts for flexible switching.
- High-Impedance Input: Ensures seamless interfacing with microcontrollers.
- Indicator LEDs: Power and channel status indicators for easy monitoring.
- Configurable Power: JD-VCC and VCC jumper for flexible power supply separation.
Principle of Work:
- Low Trigger Operation: Sending a LOW signal (0V or GND) to an input pin activates the corresponding relay.
- LED Indicators: Each channel has a status LED that lights when the relay is active.
- JD-VCC & VCC Jumper: Allows separating relay coil power from control circuit power for improved safety.
- Relay Outputs: Each relay provides NC, NO, and COM terminals for load control.
- Optical Isolation: Protects microcontrollers from high-voltage interference on the load side.
Pinout:

| Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
5V power input |
| GND |
Ground |
| INT1–INT4 |
Trigger inputs for each relay |
| JD-VCC |
Relay coil power |
| NC |
Normally Closed contact |
| COM |
Common terminal |
| NO |
Normally Open contact |
Applications:
- Home automation (lights, fans, appliances)
- Industrial and PLC control
- Security systems (door locks, alarms)
- Battery backup switching
- Energy management systems
- Automotive electrical control
Circuit Example:
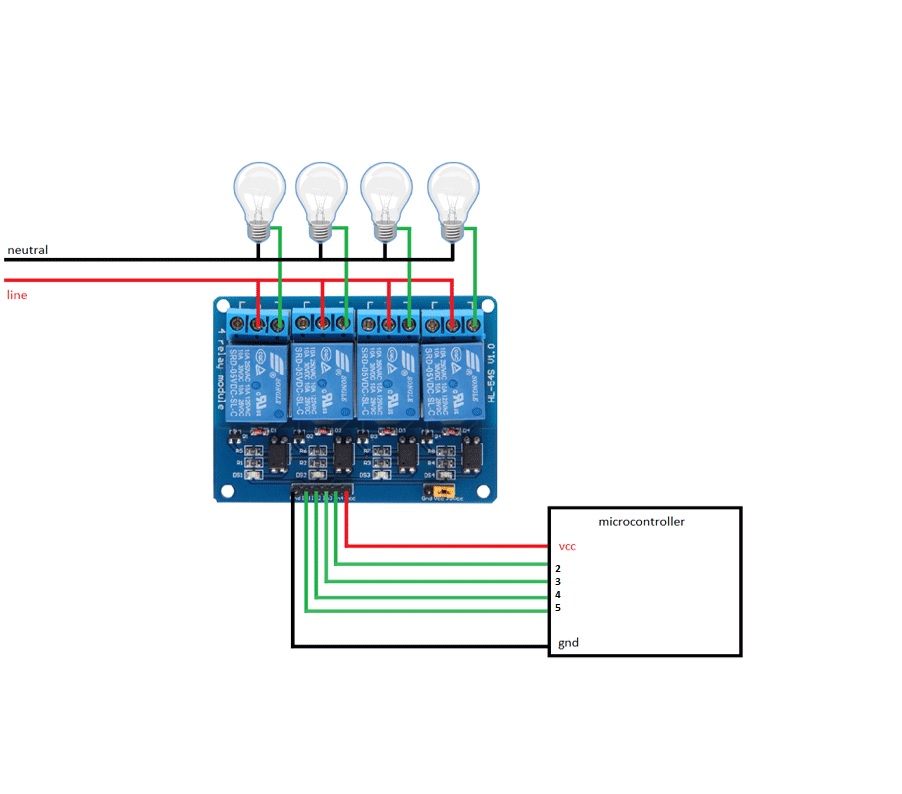
Arduino Code Example:
const int numRelays = 4;
const int relayPins[numRelays] = {2, 3, 4, 5};
const int delayTime = 1000;
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
pinMode(relayPins[i], OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], HIGH); // Relays OFF by default
}
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], LOW); // Turn ON relay
Serial.print("Relay "); Serial.print(i+1); Serial.println(" is ON");
delay(delayTime);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], HIGH); // Turn OFF relay
Serial.print("Relay "); Serial.print(i+1); Serial.println(" is OFF");
delay(delayTime);
}
}
Technical Details:
- Channels: 4
- Operating Voltage: 3.75V – 6V
- Trigger Current: 5mA – 15mA
- Active Current: ~70mA (1 relay), ~300mA (all relays)
- Relay Rating: 250VAC 10A / 30VDC 10A
- Isolation: Optical isolators onboard
Comparison: Mechanical vs SSR Relays
- Mechanical Relays: Faster response, cost-effective, shorter lifespan.
- Solid-State Relays (SSR): Noiseless, longer lifespan, compact, energy-efficient.
Features:
- Optocoupler Isolation: Reduces distortion and improves signal reliability.
- Dual Contact Design: Each relay provides Normally Closed (NC) and Normally Open (NO) contacts for flexible switching.
- High-Impedance Input: Ensures seamless interfacing with microcontrollers.
- Indicator LEDs: Power and channel status indicators for easy monitoring.
- Configurable Power: JD-VCC and VCC jumper for flexible power supply separation.
Principle of Work:
- Low Trigger Operation: Sending a LOW signal (0V or GND) to an input pin activates the corresponding relay.
- LED Indicators: Each channel has a status LED that lights when the relay is active.
- JD-VCC & VCC Jumper: Allows separating relay coil power from control circuit power for improved safety.
- Relay Outputs: Each relay provides NC, NO, and COM terminals for load control.
- Optical Isolation: Protects microcontrollers from high-voltage interference on the load side.
Pinout:

| Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
5V power input |
| GND |
Ground |
| INT1–INT4 |
Trigger inputs for each relay |
| JD-VCC |
Relay coil power |
| NC |
Normally Closed contact |
| COM |
Common terminal |
| NO |
Normally Open contact |
Applications:
- Home automation (lights, fans, appliances)
- Industrial and PLC control
- Security systems (door locks, alarms)
- Battery backup switching
- Energy management systems
- Automotive electrical control
Circuit Example:

Arduino Code Example:
const int numRelays = 4;
const int relayPins[numRelays] = {2, 3, 4, 5};
const int delayTime = 1000;
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
pinMode(relayPins[i], OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], HIGH); // Relays OFF by default
}
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], LOW); // Turn ON relay
Serial.print("Relay "); Serial.print(i+1); Serial.println(" is ON");
delay(delayTime);
}
for (int i = 0; i < numRelays; i++) {
digitalWrite(relayPins[i], HIGH); // Turn OFF relay
Serial.print("Relay "); Serial.print(i+1); Serial.println(" is OFF");
delay(delayTime);
}
}
Technical Details:
- Channels: 4
- Operating Voltage: 3.75V – 6V
- Trigger Current: 5mA – 15mA
- Active Current: ~70mA (1 relay), ~300mA (all relays)
- Relay Rating: 250VAC 10A / 30VDC 10A
- Isolation: Optical isolators onboard
Comparison: Mechanical vs SSR Relays
- Mechanical Relays: Faster response, cost-effective, shorter lifespan.
- Solid-State Relays (SSR): Noiseless, longer lifespan, compact, energy-efficient.