Features
- Built-in WiFi connectivity for wireless communication
- Dual-band antenna supporting 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks
- Supports WPA and WPA2 personal and enterprise security
- ESP8285 WiFi module with station and direct modes
- Low power consumption suitable for battery-powered projects
Principle of Operation
The Sipeed MAix BiT runs artificial intelligence algorithms locally using a dual-core 64-bit RISC-V processor. Data can be collected from connected sensors such as cameras and displays, processed on board, and then transmitted through WiFi if needed.
By processing data locally, the board reduces latency and improves system reliability. This makes it ideal for edge computing applications that require immediate decision-making.

Pinout
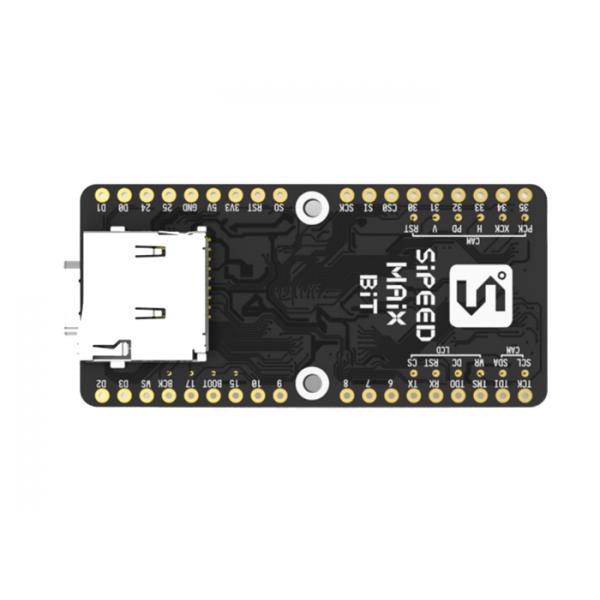


- Pin 1 V3.3 power supply 3.3V
- Pin 2 VIN power supply 4.5V to 5.5V
- Pin 3 GND ground
- Pin 4 NC reserved
- Pin 5 ADC analog input output 0 to 1.8V
- Pin 6 to 25 GPIO0 to GPIO19 general purpose IO
- Pin 26 SCK SPI clock
- Pin 27 MISO SPI master in slave out
- Pin 28 MOSI SPI master out slave in
- Pin 29 SS SPI slave select
- Pin 30 TXD UART transmit
- Pin 31 RXD UART receive
- Pin 32 NC reserved
- Pin 33 NC reserved
- Pin 34 RST reset
- Pin 35 NC reserved
- Pin 36 GND ground
Applications
- Smart home automation systems
- Industrial automation and monitoring
- Robotics and intelligent machines
- Health monitoring devices
- Environmental monitoring systems
- Low power edge computing platforms
- Educational AI and IoT projects
Example Circuit
To blink an LED, connect the LED anode to a GPIO pin and the cathode to ground. Power the board using a USB Type C cable.
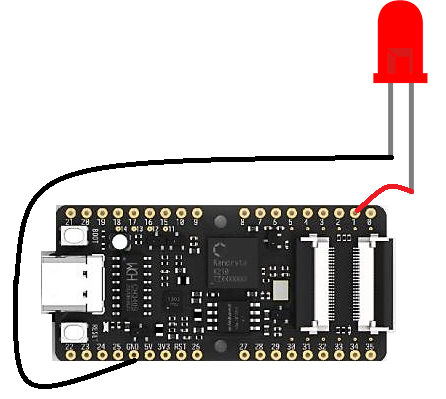
Firmware and Library
No additional libraries are required for basic examples. The MaixPy firmware must be installed before use. Drivers and firmware can be downloaded from the Sipeed repository.
LED Blink Code Example
from machine import Pin
import time
led_pin = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
while True:
led_pin.value(1)
time.sleep(0.5)
led_pin.value(0)
time.sleep(0.5)
Technical Details
- Processor dual core 64 bit RISC V up to 400 MHz
- High speed UART and JTAG debugging support
- All GPIO pins available on 2 by 20 header
- Micro SD card slot for external storage
- USB Type C with one click download support
- DVP camera connector for image processing
- LCD connector for external displays
- Reset and user buttons on board
Comparison with ESP32 NodeMCU
- MAix BiT uses a RISC V dual core processor while ESP32 uses Tensilica LX6
- MAix BiT includes AI acceleration while ESP32 does not
- MAix BiT provides more memory for AI workloads
- ESP32 supports BLE while MAix BiT supports classic Bluetooth
- ESP32 is lower cost while MAix BiT targets AI focused applications
Features
- Built-in WiFi connectivity for wireless communication
- Dual-band antenna supporting 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks
- Supports WPA and WPA2 personal and enterprise security
- ESP8285 WiFi module with station and direct modes
- Low power consumption suitable for battery-powered projects
Principle of Operation
The Sipeed MAix BiT runs artificial intelligence algorithms locally using a dual-core 64-bit RISC-V processor. Data can be collected from connected sensors such as cameras and displays, processed on board, and then transmitted through WiFi if needed.
By processing data locally, the board reduces latency and improves system reliability. This makes it ideal for edge computing applications that require immediate decision-making.

Pinout


- Pin 1 V3.3 power supply 3.3V
- Pin 2 VIN power supply 4.5V to 5.5V
- Pin 3 GND ground
- Pin 4 NC reserved
- Pin 5 ADC analog input output 0 to 1.8V
- Pin 6 to 25 GPIO0 to GPIO19 general purpose IO
- Pin 26 SCK SPI clock
- Pin 27 MISO SPI master in slave out
- Pin 28 MOSI SPI master out slave in
- Pin 29 SS SPI slave select
- Pin 30 TXD UART transmit
- Pin 31 RXD UART receive
- Pin 32 NC reserved
- Pin 33 NC reserved
- Pin 34 RST reset
- Pin 35 NC reserved
- Pin 36 GND ground
Applications
- Smart home automation systems
- Industrial automation and monitoring
- Robotics and intelligent machines
- Health monitoring devices
- Environmental monitoring systems
- Low power edge computing platforms
- Educational AI and IoT projects
Example Circuit
To blink an LED, connect the LED anode to a GPIO pin and the cathode to ground. Power the board using a USB Type C cable.

Firmware and Library
No additional libraries are required for basic examples. The MaixPy firmware must be installed before use. Drivers and firmware can be downloaded from the Sipeed repository.
LED Blink Code Example
from machine import Pin
import time
led_pin = Pin(4, Pin.OUT)
while True:
led_pin.value(1)
time.sleep(0.5)
led_pin.value(0)
time.sleep(0.5)
Technical Details
- Processor dual core 64 bit RISC V up to 400 MHz
- High speed UART and JTAG debugging support
- All GPIO pins available on 2 by 20 header
- Micro SD card slot for external storage
- USB Type C with one click download support
- DVP camera connector for image processing
- LCD connector for external displays
- Reset and user buttons on board
Comparison with ESP32 NodeMCU
- MAix BiT uses a RISC V dual core processor while ESP32 uses Tensilica LX6
- MAix BiT includes AI acceleration while ESP32 does not
- MAix BiT provides more memory for AI workloads
- ESP32 supports BLE while MAix BiT supports classic Bluetooth
- ESP32 is lower cost while MAix BiT targets AI focused applications