Specification:
Material: Zinc Sheet
Application: Experiment Electrode for Fruit Battery
Size: 10 × 40 mm
Thickness: 0.3 mm (Copper layer)
Chemistry Behind Zinc-Based Galvanic Cells
A battery is a device made of one or more galvanic cells used to store and produce electric energy via chemical reactions. Each galvanic cell has two half-cells: one for reduction and one for oxidation. Zinc is commonly used as the anode (oxidation electrode) in these cells.
In a typical fruit battery, the zinc electrode undergoes oxidation:
Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox)
In electrochemistry, oxidation means the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons. This can be remembered as LEO (Lose Electrons = Oxidation) and GER (Gain Electrons = Reduction).
Zinc acts as the reducing agent in the reaction, donating electrons to complete the circuit when paired with a suitable oxidizing agent such as copper.
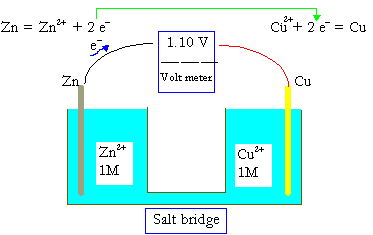
Example: Copper-Zinc Voltaic Cell
In a simple voltaic cell, zinc serves as the anode and copper as the cathode. The spontaneous redox reaction between them generates electricity.
Zinc Reaction: Zn (s) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻
Copper Reaction: Cu²⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu (s)
The flow of electrons from zinc to copper provides usable electric current in educational battery experiments.
Specification:
Material: Zinc Sheet
Application: Experiment Electrode for Fruit Battery
Size: 10 × 40 mm
Thickness: 0.3 mm (Copper layer)
Chemistry Behind Zinc-Based Galvanic Cells
A battery is a device made of one or more galvanic cells used to store and produce electric energy via chemical reactions. Each galvanic cell has two half-cells: one for reduction and one for oxidation. Zinc is commonly used as the anode (oxidation electrode) in these cells.
In a typical fruit battery, the zinc electrode undergoes oxidation:
Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Redox)
In electrochemistry, oxidation means the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons. This can be remembered as LEO (Lose Electrons = Oxidation) and GER (Gain Electrons = Reduction).
Zinc acts as the reducing agent in the reaction, donating electrons to complete the circuit when paired with a suitable oxidizing agent such as copper.
Example: Copper-Zinc Voltaic Cell
In a simple voltaic cell, zinc serves as the anode and copper as the cathode. The spontaneous redox reaction between them generates electricity.
Zinc Reaction: Zn (s) → Zn²⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻
Copper Reaction: Cu²⁺ (aq) + 2e⁻ → Cu (s)
The flow of electrons from zinc to copper provides usable electric current in educational battery experiments.


