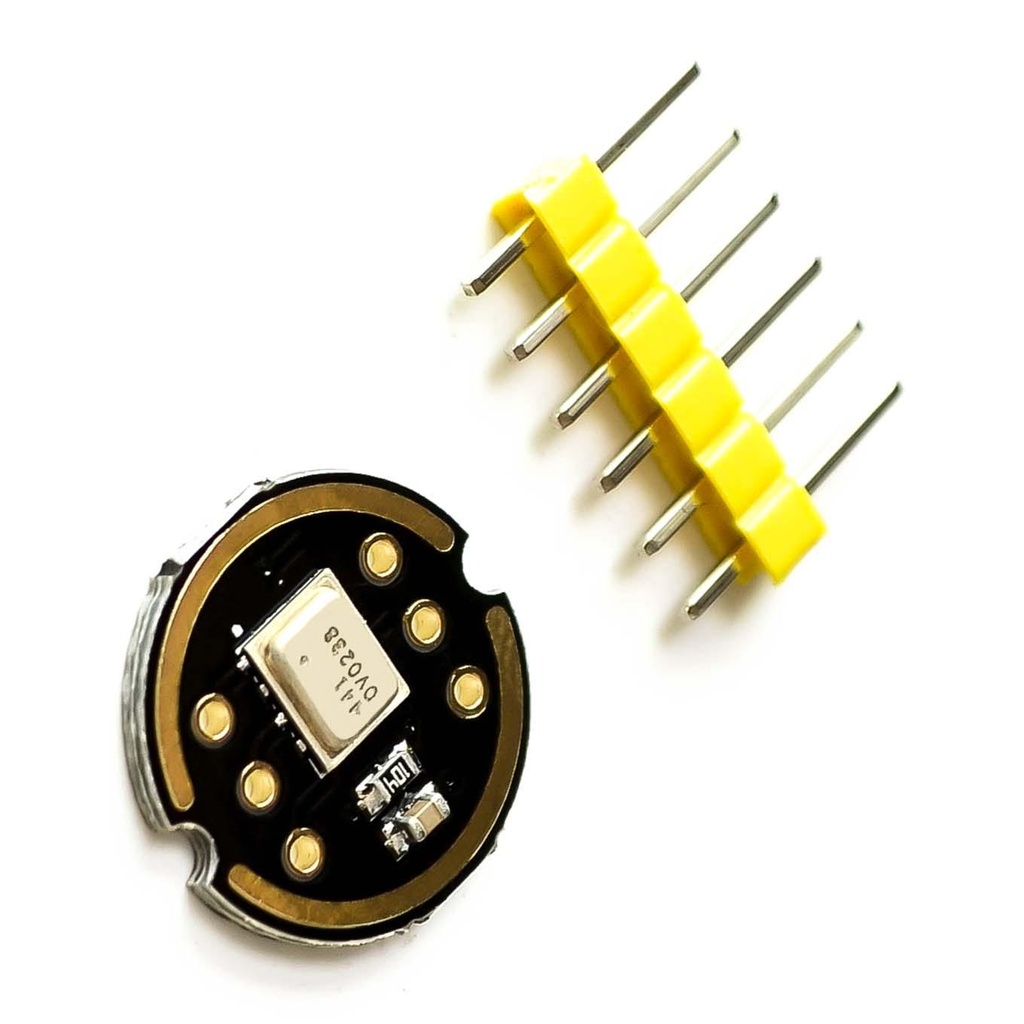
Features:
- Low noise
- Low power consumption
- Suitable for various electronic products
- Stereo input capability (Left/Right channels)
- Omnidirectional microphone response
- 24-bit I2S digital output
Principle of Work:
Sampling high-quality audio requires sample rates of 16-40 KHz. While you can use a timer to sample the ADC directly, this is inefficient for ESP32 CPU usage. Instead, the built-in I2S interface reads samples from the ADC directly into memory via DMA buffers in the background, enabling efficient continuous audio capture.
Pinout:
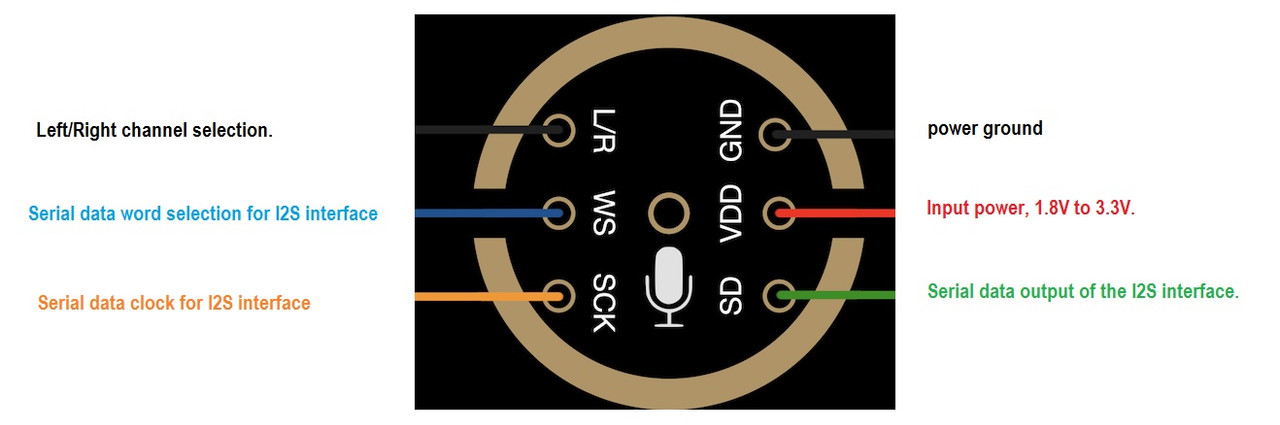
- SCK: Serial clock for I2S interface
- WS: Word select for I2S (frame sync)
- L/R: Left/Right channel select (Low = left channel, High = right channel)
- SD: Serial data output
- VCC: Power supply, 1.8V to 3.3V
- GND: Ground
Channel Selection (L/R pin):
- LEFT – Connect L/R to GND
- RIGHT – Connect L/R to VDD
Applications:
- Noise detectors
- Voice control modules
- Sound recorders
- Activity monitors
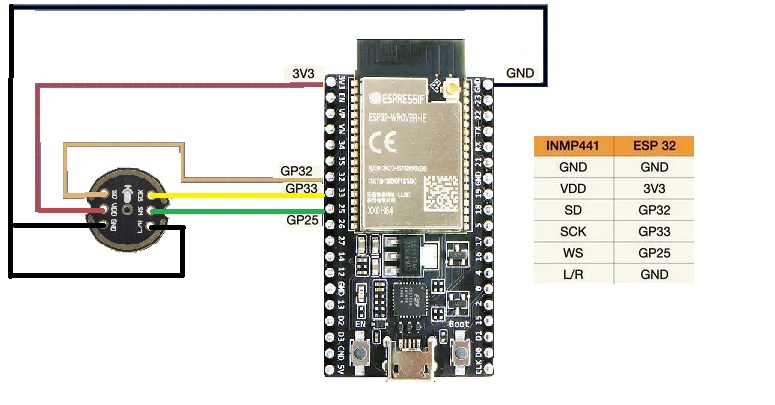
Circuit Example with ESP32:
Below is a simple wiring diagram connecting the INMP441 module to an ESP32. Use GPIO numbers for connections, as ESP32 pinouts may vary.
Library:
The ESP32 Arduino core includes an I2S driver library by default, which supports communication with the INMP441 module.
Example Code (Arduino IDE):
// Include I2S driver
#include "driver/i2s.h"
// INMP441 I2S microphone pins
#define I2S_WS 25
#define I2S_SD 33
#define I2S_SCK 32
#define I2S_PORT I2S_NUM_0
#define bufferLen 64
int16_t sBuffer[bufferLen];
void i2s_install() {
const i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
.mode = i2s_mode_t(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX),
.sample_rate = 44100,
.bits_per_sample = i2s_bits_per_sample_t(16),
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT,
.communication_format = i2s_comm_format_t(I2S_COMM_FORMAT_STAND_I2S),
.intr_alloc_flags = 0,
.dma_buf_count = 8,
.dma_buf_len = bufferLen,
.use_apll = false
};
i2s_driver_install(I2S_PORT, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
}
void i2s_setpin() {
const i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
.bck_io_num = I2S_SCK,
.ws_io_num = I2S_WS,
.data_out_num = -1,
.data_in_num = I2S_SD
};
i2s_set_pin(I2S_PORT, &pin_config);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
i2s_install();
i2s_setpin();
i2s_start(I2S_PORT);
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
int rangelimit = 3000;
Serial.print(rangelimit * -1);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(rangelimit);
Serial.print(" ");
size_t bytesIn = 0;
esp_err_t result = i2s_read(I2S_PORT, &sBuffer, bufferLen * sizeof(int16_t), &bytesIn, portMAX_DELAY);
if (result == ESP_OK) {
int16_t samples_read = bytesIn / sizeof(int16_t);
if (samples_read > 0) {
float mean = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < samples_read; i++) {
mean += sBuffer[i];
}
mean /= samples_read;
Serial.println(mean);
}
}
}
Technical Details:
- Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): 61 dBA
- Frequency response: 60 Hz – 15 kHz
- Board size: 14 mm diameter, low profile
- Sensitivity: -26 dBFS at 1 kHz, 94 dB input
- Noise floor: -87 dBFS
- Supported sample rates: 44.1 kHz to 48 kHz
Resources:
Comparisons:
Omnidirectional microphones like the INMP441 have a wide pickup radius (up to several meters), making them sensitive to multiple voices and background noise. While excellent for informal meetings, short-distance conversations, and remote activities, their sound quality can be lower than single-point microphones unless effective noise reduction is implemented.
Features:
- Low noise
- Low power consumption
- Suitable for various electronic products
- Stereo input capability (Left/Right channels)
- Omnidirectional microphone response
- 24-bit I2S digital output
Principle of Work:
Sampling high-quality audio requires sample rates of 16-40 KHz. While you can use a timer to sample the ADC directly, this is inefficient for ESP32 CPU usage. Instead, the built-in I2S interface reads samples from the ADC directly into memory via DMA buffers in the background, enabling efficient continuous audio capture.
Pinout:

- SCK: Serial clock for I2S interface
- WS: Word select for I2S (frame sync)
- L/R: Left/Right channel select (Low = left channel, High = right channel)
- SD: Serial data output
- VCC: Power supply, 1.8V to 3.3V
- GND: Ground
Channel Selection (L/R pin):
- LEFT – Connect L/R to GND
- RIGHT – Connect L/R to VDD
Applications:
- Noise detectors
- Voice control modules
- Sound recorders
- Activity monitors
Circuit Example with ESP32:
Below is a simple wiring diagram connecting the INMP441 module to an ESP32. Use GPIO numbers for connections, as ESP32 pinouts may vary.

Library:
The ESP32 Arduino core includes an I2S driver library by default, which supports communication with the INMP441 module.
Example Code (Arduino IDE):
// Include I2S driver
#include "driver/i2s.h"
// INMP441 I2S microphone pins
#define I2S_WS 25
#define I2S_SD 33
#define I2S_SCK 32
#define I2S_PORT I2S_NUM_0
#define bufferLen 64
int16_t sBuffer[bufferLen];
void i2s_install() {
const i2s_config_t i2s_config = {
.mode = i2s_mode_t(I2S_MODE_MASTER | I2S_MODE_RX),
.sample_rate = 44100,
.bits_per_sample = i2s_bits_per_sample_t(16),
.channel_format = I2S_CHANNEL_FMT_ONLY_LEFT,
.communication_format = i2s_comm_format_t(I2S_COMM_FORMAT_STAND_I2S),
.intr_alloc_flags = 0,
.dma_buf_count = 8,
.dma_buf_len = bufferLen,
.use_apll = false
};
i2s_driver_install(I2S_PORT, &i2s_config, 0, NULL);
}
void i2s_setpin() {
const i2s_pin_config_t pin_config = {
.bck_io_num = I2S_SCK,
.ws_io_num = I2S_WS,
.data_out_num = -1,
.data_in_num = I2S_SD
};
i2s_set_pin(I2S_PORT, &pin_config);
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
delay(1000);
i2s_install();
i2s_setpin();
i2s_start(I2S_PORT);
delay(500);
}
void loop() {
int rangelimit = 3000;
Serial.print(rangelimit * -1);
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(rangelimit);
Serial.print(" ");
size_t bytesIn = 0;
esp_err_t result = i2s_read(I2S_PORT, &sBuffer, bufferLen * sizeof(int16_t), &bytesIn, portMAX_DELAY);
if (result == ESP_OK) {
int16_t samples_read = bytesIn / sizeof(int16_t);
if (samples_read > 0) {
float mean = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < samples_read; i++) {
mean += sBuffer[i];
}
mean /= samples_read;
Serial.println(mean);
}
}
}
Technical Details:
- Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR): 61 dBA
- Frequency response: 60 Hz – 15 kHz
- Board size: 14 mm diameter, low profile
- Sensitivity: -26 dBFS at 1 kHz, 94 dB input
- Noise floor: -87 dBFS
- Supported sample rates: 44.1 kHz to 48 kHz
Resources:
Comparisons:
Omnidirectional microphones like the INMP441 have a wide pickup radius (up to several meters), making them sensitive to multiple voices and background noise. While excellent for informal meetings, short-distance conversations, and remote activities, their sound quality can be lower than single-point microphones unless effective noise reduction is implemented.