Features:
- Charging Current: Up to 1A for fast and safe charging.
- Charging Voltage: Max 4.2V with ±1.5% accuracy.
- Input Voltage: 4.5V–5.5V (via USB-C or solder pads).
- LED Indicators:
- LED near R2: Charging in progress
- LED near R1: Fully charged
- Battery Protection:
- Stops charging if battery voltage < 2.5V
- Stops charging if current > 3A
- Battery Compatibility: Suitable for Li-ion or Li-Po batteries (charge to 4.2V, discharge to 2.5V).
- Chipset: TP4056 or TC4056(A) for stable and safe charging.
- Compact Size: Only 29 x 17 x 4 mm – perfect for tight spaces.
Principle of Work:
The TP4056 board uses a CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) charging algorithm. It begins by supplying a constant current to the battery, gradually increasing the voltage. Once the battery reaches 4.2V, it switches to constant voltage mode, reducing the current until the battery is fully charged. Protection circuitry prevents overcharging or unsafe discharge conditions.
Pinout of the Module:
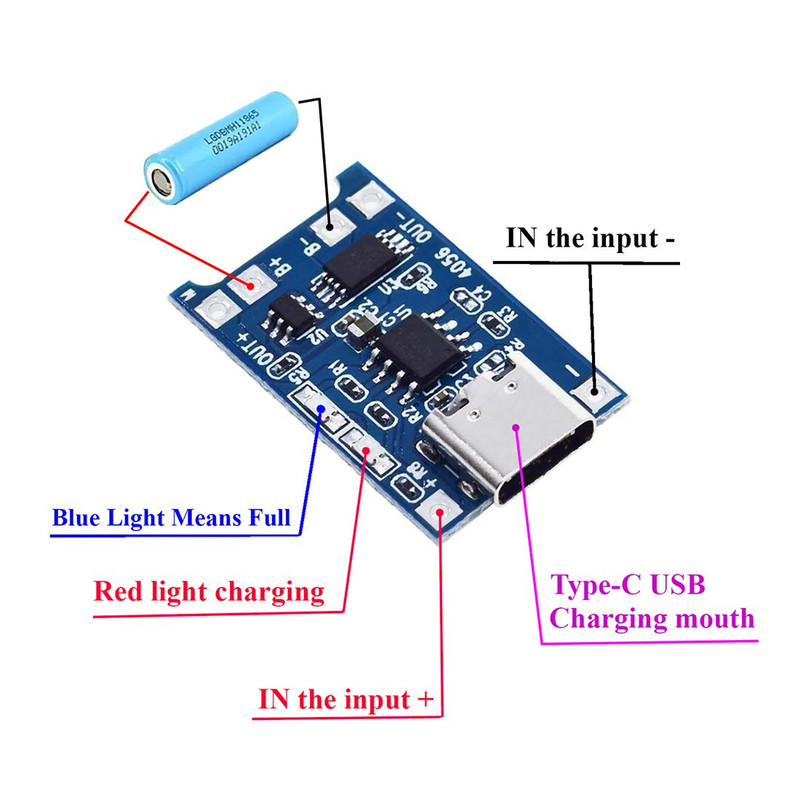
- B+: Connect to battery positive terminal
- B-: Connect to battery negative terminal
- OUT+: Positive output terminal
- OUT-: Negative output terminal
- IN+: Charger positive input
- IN-: Charger negative input
Applications:
- Portable devices (smartphones, tablets, speakers)
- DIY power banks
- LED lighting systems
- Small robotics and IoT devices
- General hobby and electronics projects
Circuit:
Simply connect the battery as shown in the pinout image and use a USB-C cable to begin charging. No external libraries or code are required.
Comparison: TP4056 vs CN3065
- Charging Current: TP4056: 1A | CN3065: up to 3A
- Input Voltage: TP4056: 4.5V–5.5V | CN3065: up to 26V
- Output Voltage: TP4056: Fixed 4.2V | CN3065: Adjustable 3.3V–22V
- Protection: Both offer overcharge/discharge; CN3065 adds short-circuit & overcurrent
- Cost: TP4056 is more affordable for low-power applications
Conclusion: TP4056 is best for compact, low-power designs, while CN3065 is better for high-power and variable voltage needs.
Features:
- Charging Current: Up to 1A for fast and safe charging.
- Charging Voltage: Max 4.2V with ±1.5% accuracy.
- Input Voltage: 4.5V–5.5V (via USB-C or solder pads).
- LED Indicators:
- LED near R2: Charging in progress
- LED near R1: Fully charged
- Battery Protection:
- Stops charging if battery voltage < 2.5V
- Stops charging if current > 3A
- Battery Compatibility: Suitable for Li-ion or Li-Po batteries (charge to 4.2V, discharge to 2.5V).
- Chipset: TP4056 or TC4056(A) for stable and safe charging.
- Compact Size: Only 29 x 17 x 4 mm – perfect for tight spaces.
Principle of Work:
The TP4056 board uses a CC/CV (Constant Current/Constant Voltage) charging algorithm. It begins by supplying a constant current to the battery, gradually increasing the voltage. Once the battery reaches 4.2V, it switches to constant voltage mode, reducing the current until the battery is fully charged. Protection circuitry prevents overcharging or unsafe discharge conditions.
Pinout of the Module:

- B+: Connect to battery positive terminal
- B-: Connect to battery negative terminal
- OUT+: Positive output terminal
- OUT-: Negative output terminal
- IN+: Charger positive input
- IN-: Charger negative input
Applications:
- Portable devices (smartphones, tablets, speakers)
- DIY power banks
- LED lighting systems
- Small robotics and IoT devices
- General hobby and electronics projects
Circuit:
Simply connect the battery as shown in the pinout image and use a USB-C cable to begin charging. No external libraries or code are required.
Comparison: TP4056 vs CN3065
- Charging Current: TP4056: 1A | CN3065: up to 3A
- Input Voltage: TP4056: 4.5V–5.5V | CN3065: up to 26V
- Output Voltage: TP4056: Fixed 4.2V | CN3065: Adjustable 3.3V–22V
- Protection: Both offer overcharge/discharge; CN3065 adds short-circuit & overcurrent
- Cost: TP4056 is more affordable for low-power applications
Conclusion: TP4056 is best for compact, low-power designs, while CN3065 is better for high-power and variable voltage needs.

