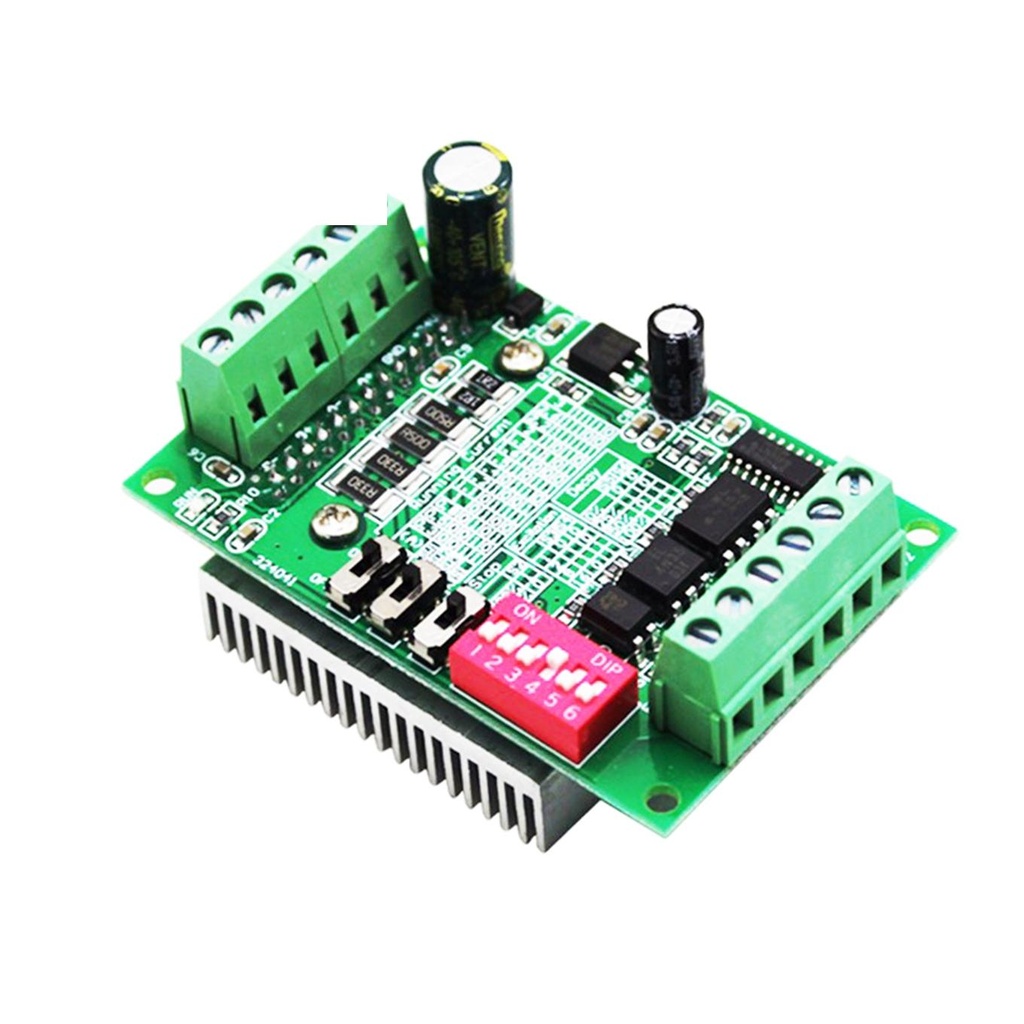
Features:
- Optocoupler Isolation: High-speed optocoupler (6N137) ensures precise and stable input signal isolation.
- Heat Dissipation: Large heat sink allows for effective thermal management, extending component life.
- Adjustable Semi-Flow Mode & Current: Fine-tune motor behavior and current output for your specific needs.
- Overheat & Overcurrent Protection: Integrated protection safeguards your driver and motor.
- Wide Input Voltage Range: Operates from DC 10V to 35V (recommended: 24V).
- Supports 2/4-phase Motors: Compatible with 4-wire and 6-wire stepper motors up to 3A.
- Multiple Excitation Modes: Includes full, half, 1/8, and 1/16 step modes (up to 16 segments).
Specifications:
- Working Voltage: DC 10V–35V (Recommended: DC 24V)
- OptoCoupler: 6N137 High-Speed Isolation
- Main Driver IC: Toshiba TB6560AHQ
- Output Current: ±3A (Peak 3.5A)
- Supported Motors: 2/4-phase, 4-wire or 6-wire stepper motors up to 3A
- Excitation Modes: Full step, half step, 1/8 step, 1/16 step (up to 16 segments)
- Board Dimensions: 50 x 75 x 35 mm
Connection Table:
| Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
10 – 35 VDC |
| GND |
Power supply ground |
| EN+ |
Not connected |
| EN− |
Not connected |
| CW+ |
Arduino Pin 2 |
| CW− |
Arduino GND |
| CLK+ |
Arduino Pin 3 |
| CLK− |
Arduino GND |
| A+, A− |
Stepper Motor Coil 1 |
| B+, B− |
Stepper Motor Coil 2 |
Wiring Diagram:

Sample Arduino Code:
#define dirPin 2
#define stepPin 3
#define stepsPerRevolution 1600
void setup() {
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Clockwise rotation - slow
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH);
for (int i = 0; i < stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(2000);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2000);
}
delay(1000);
// Counterclockwise - fast
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
delay(1000);
// Clockwise - 5 fast revolutions
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH);
for (int i = 0; i < 5 * stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000);
// Counterclockwise - 5 fast revolutions
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < 5 * stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000);
}
Features:
- Optocoupler Isolation: High-speed optocoupler (6N137) ensures precise and stable input signal isolation.
- Heat Dissipation: Large heat sink allows for effective thermal management, extending component life.
- Adjustable Semi-Flow Mode & Current: Fine-tune motor behavior and current output for your specific needs.
- Overheat & Overcurrent Protection: Integrated protection safeguards your driver and motor.
- Wide Input Voltage Range: Operates from DC 10V to 35V (recommended: 24V).
- Supports 2/4-phase Motors: Compatible with 4-wire and 6-wire stepper motors up to 3A.
- Multiple Excitation Modes: Includes full, half, 1/8, and 1/16 step modes (up to 16 segments).
Specifications:
- Working Voltage: DC 10V–35V (Recommended: DC 24V)
- OptoCoupler: 6N137 High-Speed Isolation
- Main Driver IC: Toshiba TB6560AHQ
- Output Current: ±3A (Peak 3.5A)
- Supported Motors: 2/4-phase, 4-wire or 6-wire stepper motors up to 3A
- Excitation Modes: Full step, half step, 1/8 step, 1/16 step (up to 16 segments)
- Board Dimensions: 50 x 75 x 35 mm
Connection Table:
| Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
10 – 35 VDC |
| GND |
Power supply ground |
| EN+ |
Not connected |
| EN− |
Not connected |
| CW+ |
Arduino Pin 2 |
| CW− |
Arduino GND |
| CLK+ |
Arduino Pin 3 |
| CLK− |
Arduino GND |
| A+, A− |
Stepper Motor Coil 1 |
| B+, B− |
Stepper Motor Coil 2 |
Wiring Diagram:

Sample Arduino Code:
#define dirPin 2
#define stepPin 3
#define stepsPerRevolution 1600
void setup() {
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Clockwise rotation - slow
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH);
for (int i = 0; i < stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(2000);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2000);
}
delay(1000);
// Counterclockwise - fast
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(1000);
}
delay(1000);
// Clockwise - 5 fast revolutions
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH);
for (int i = 0; i < 5 * stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000);
// Counterclockwise - 5 fast revolutions
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < 5 * stepsPerRevolution; i++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000);
}