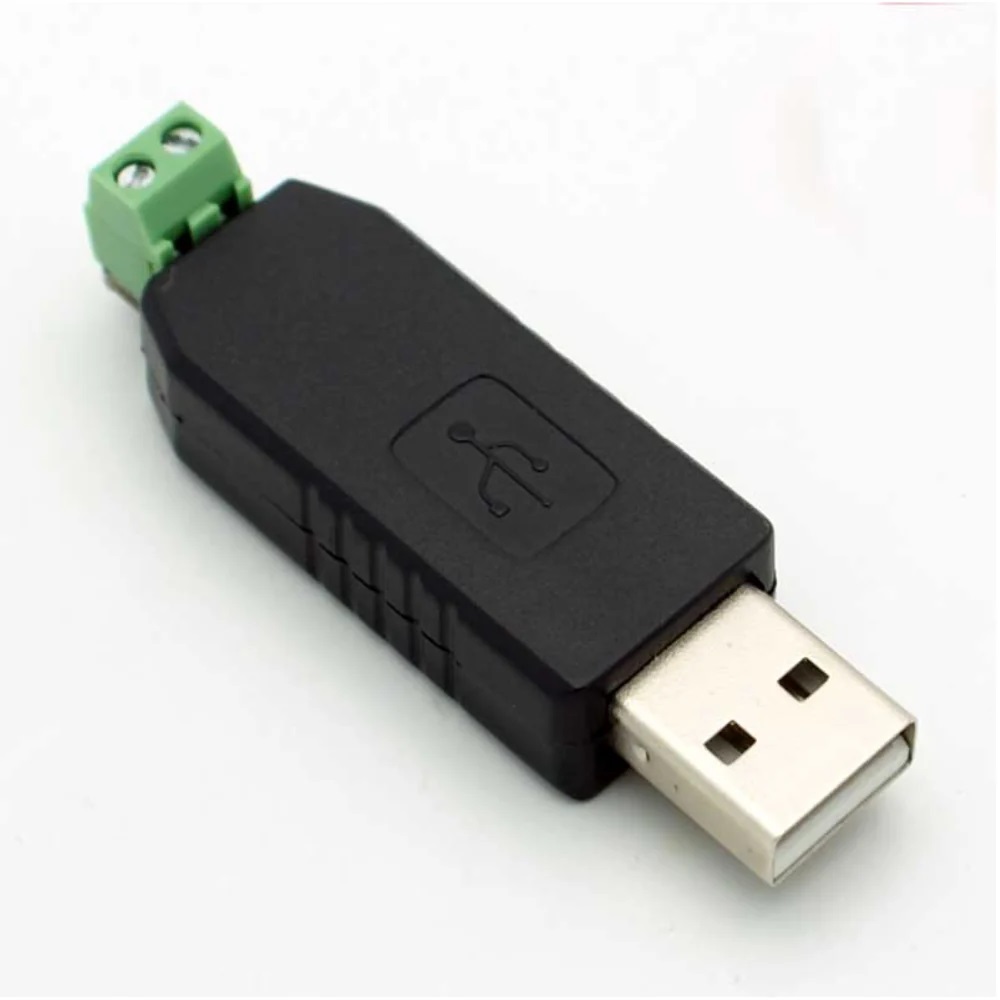
Features:
- Easy Connectivity: Simplifies connecting serial devices to a USB port.
- RS-485 Communication: Supports RS-485 standard for industrial and automation applications.
- Screw Terminals: Easy wire connection; backward compatible with USB 1.1.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Supports baud rates from 75bps to 115200bps and speeds up to 6 Mbps.
- Low Power Consumption: No external power supply needed.
- Operating System Compatibility: Works with Windows XP/Vista/7/8, Mac, Linux, Windows CE 5.0.
- Compact Design: Dimensions of 60 x 18 x 14mm, easy to carry and use.
- Raspberry Pi Compatible: No driver required, ideal for Pi projects.
Specifications:
- Communication Interface: USB to RS-485
- Connection: Screw terminals
- Baud Rates: 75bps to 115200bps, up to 6 Mbps
- Power: Powered via USB, no external power needed
- Operating Systems: Windows XP/Vista/7/8, Mac, Linux, Windows CE 5.0
- Dimensions: 60 x 18 x 14 mm
- Color: Black
Pinout of the Module:
- A or D+: Positive RS-485 signal
- B or D-: Negative RS-485 signal

Applications:
- Connecting Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to computers for monitoring and control.
- Connecting sensors, meters, motor controllers, and other serial RS485 devices.
- Protocol gateways between Modbus TCP/IP and Modbus RTU.
- Building automation, access control, and industrial process control systems.
- Cost-effective solution for connecting multiple RS485 devices to a PC or embedded system.
Working Principle:
The device converts USB communication signals into RS485 differential signals via its integrated chip. When connected to a PC, it communicates over USB and transmits converted signals on the RS485 bus through its A and B lines. Incoming RS485 signals are converted back to USB data for the host system.
Example Circuit:
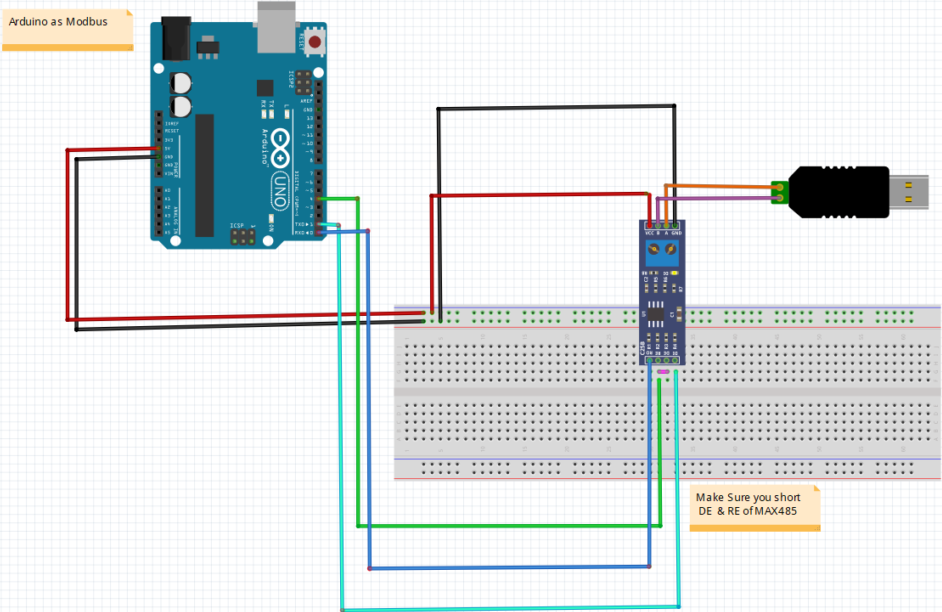
An Arduino UNO can be configured as a Modbus slave connected to the PC via the USB RS485 adapter. The Arduino uses an RS485 TTL to RS485 converter module to communicate over the RS485 bus.
Arduino Modbus Slave Code Sample:
#include "ModbusRtu.h"
Modbus bus;
uint16_t modbus_array[] = {0, 0, 0};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Hello");
Serial.println("Arduino Slave");
delay(5000);
bus = Modbus(1, 1, 4); // Slave ID 1, RX pin 1, DE/RE pin 4
bus.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
bus.poll(modbus_array, sizeof(modbus_array) / sizeof(modbus_array[0]));
if (modbus_array[0] == 0)
Serial.println("Data 1");
else
Serial.println("NO Data 1");
if (modbus_array[1] == 0)
Serial.println("Data 2");
else
Serial.println("NO Data 2");
int pwm = modbus_array[2];
Serial.print("Mod bus: ");
Serial.println(pwm);
delay(200);
}
Features:
- Easy Connectivity: Simplifies connecting serial devices to a USB port.
- RS-485 Communication: Supports RS-485 standard for industrial and automation applications.
- Screw Terminals: Easy wire connection; backward compatible with USB 1.1.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: Supports baud rates from 75bps to 115200bps and speeds up to 6 Mbps.
- Low Power Consumption: No external power supply needed.
- Operating System Compatibility: Works with Windows XP/Vista/7/8, Mac, Linux, Windows CE 5.0.
- Compact Design: Dimensions of 60 x 18 x 14mm, easy to carry and use.
- Raspberry Pi Compatible: No driver required, ideal for Pi projects.
Specifications:
- Communication Interface: USB to RS-485
- Connection: Screw terminals
- Baud Rates: 75bps to 115200bps, up to 6 Mbps
- Power: Powered via USB, no external power needed
- Operating Systems: Windows XP/Vista/7/8, Mac, Linux, Windows CE 5.0
- Dimensions: 60 x 18 x 14 mm
- Color: Black
Pinout of the Module:
- A or D+: Positive RS-485 signal
- B or D-: Negative RS-485 signal

Applications:
- Connecting Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) to computers for monitoring and control.
- Connecting sensors, meters, motor controllers, and other serial RS485 devices.
- Protocol gateways between Modbus TCP/IP and Modbus RTU.
- Building automation, access control, and industrial process control systems.
- Cost-effective solution for connecting multiple RS485 devices to a PC or embedded system.
Working Principle:
The device converts USB communication signals into RS485 differential signals via its integrated chip. When connected to a PC, it communicates over USB and transmits converted signals on the RS485 bus through its A and B lines. Incoming RS485 signals are converted back to USB data for the host system.
Example Circuit:

An Arduino UNO can be configured as a Modbus slave connected to the PC via the USB RS485 adapter. The Arduino uses an RS485 TTL to RS485 converter module to communicate over the RS485 bus.
Arduino Modbus Slave Code Sample:
#include "ModbusRtu.h"
Modbus bus;
uint16_t modbus_array[] = {0, 0, 0};
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Hello");
Serial.println("Arduino Slave");
delay(5000);
bus = Modbus(1, 1, 4); // Slave ID 1, RX pin 1, DE/RE pin 4
bus.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
bus.poll(modbus_array, sizeof(modbus_array) / sizeof(modbus_array[0]));
if (modbus_array[0] == 0)
Serial.println("Data 1");
else
Serial.println("NO Data 1");
if (modbus_array[1] == 0)
Serial.println("Data 2");
else
Serial.println("NO Data 2");
int pwm = modbus_array[2];
Serial.print("Mod bus: ");
Serial.println(pwm);
delay(200);
}


