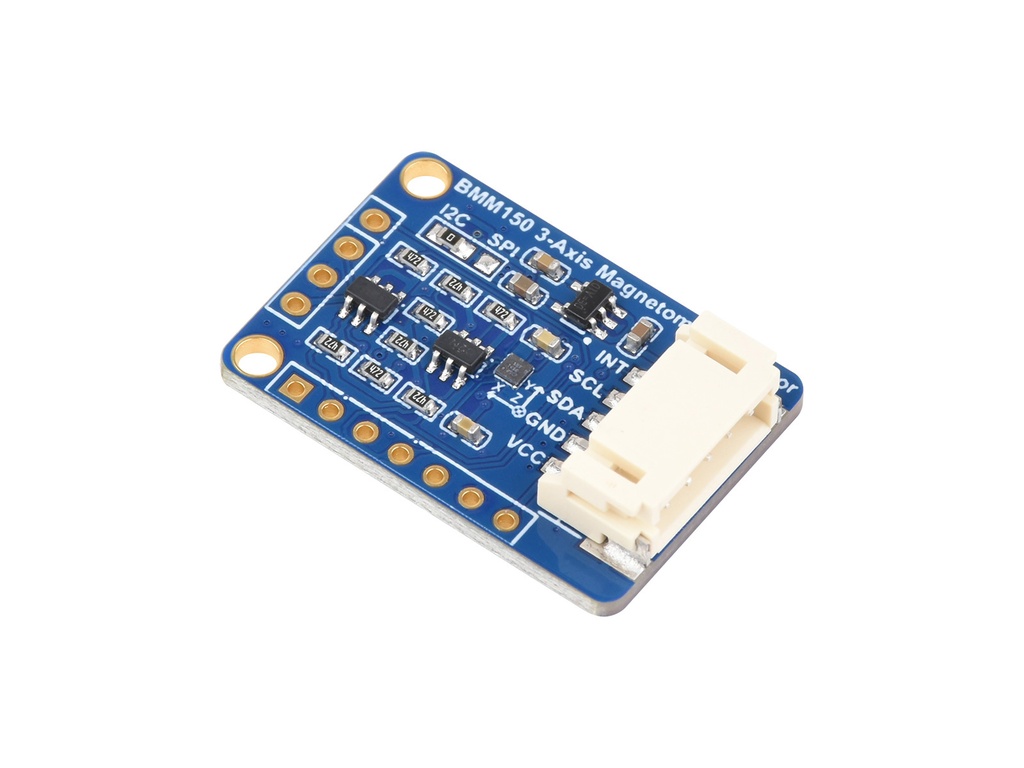
Features:
- Compact Form Factor: Ultra-small design for easy integration in space-constrained projects.
- Energy Efficiency: Low power consumption for prolonged operational hours.
- Precision and Reliability: Ultra-low noise guarantees accurate altitude measurements.
- Versatile Connectivity: Supports both I2C and SPI interfaces.
- Voltage Adaptability: Compatible with 3.3V and 5V systems.
Principle of Work
Internal Operation:
- Magnetometer Sensor Elements: Three sensor elements measure the magnetic field along X, Y, and Z axes using the Hall effect.
- Magnetic Field Measurement: Continuously measures strength and direction along all axes.
- Analog to Digital Conversion: Converts analog Hall effect signals into digital data.
- Data Processing: Calculates net magnetic field vector with error and temperature compensation.
- Output: Digital data available via I2C or SPI interfaces.
Interaction with MCU:
- Initialization: MCU sends setup commands via I2C or SPI.
- Data Retrieval: MCU reads magnetic field data along X, Y, Z axes.
- Data Processing: MCU calibrates and converts raw data, optionally fusing with accelerometer/gyroscope data.
- Algorithm Integration: Determine orientation or heading relative to Earth's magnetic field.
- Application-Specific Functions: Digital compass, drone navigation, augmented reality heading info, etc.
Module Pinout:

| Pin |
Description |
Additional Information |
| VCC |
Power input |
Provides voltage to the sensor. |
| GND |
Ground |
Electrical ground reference. |
| SDA |
I2C Data |
I2C data line. |
| SCL |
I2C Clock |
I2C clock line. |
| INT |
Interrupt Output |
Connect to I/O pin for event signaling. |
| SDO |
SPI Data Out (MISO) |
Data from sensor to host. |
| SDI |
SPI Data In (MOSI) |
Data from host to sensor. |
| CS |
Chip Selection |
Enable/disable sensor communication. |
| DRY |
Data Ready |
Signals when sensor is ready to send/receive data. |
Applications:
- Wearables: Altitude monitoring for fitness and outdoor tracking.
- Audible Devices: Elevation-based navigation or audio applications.
- Drones: Precise altitude measurements for stable flight.
- Altimeters: Accurate altitude readings for any device.
- Environmental Monitoring: Real-time data for research and studies.
- IoT Projects: Enhances IoT applications with critical altitude data.
Circuit Connection:
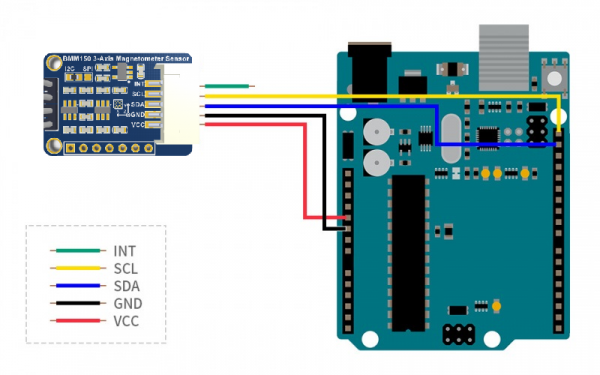
| Module Pin |
Arduino Uno Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
5V |
Power input connection. |
| GND |
GND |
Ground connection. |
| SDA |
SDA |
I2C data line. |
| SCL |
SCL |
I2C clock line. |
| INT |
NC |
No connection; optional interrupt usage. |
Library & Code:
Download the example demo and copy the Arduino folder into your code directory. The included sketch initializes the BMM150, reads magnetic data along X, Y, Z axes, and prints results to the serial monitor.
Technical Details:
- Operating voltage: 3.3V / 5V
- Communication interface: I2C / SPI
- Resolution: 0.3 μT
- Linearity: <1% FS
- Gain error: ±2%
- Temperature drift: ±0.01% / K
- Zero point drift: ±40 μT (25°C)
- Measuring range: ±1300 μT (X,Y), ±2500 μT (Z)
- Data output rate: 10 Hz (normal mode)
- Operating temperature: -40~85°C
- Dimensions: 29mm × 20mm
Comparisons:
| Aspect |
BMM150 |
BME280 |
| Type |
3-Axis Magnetometer |
Environmental Sensor (3-in-1) |
| Functionality |
Measures magnetic fields in 3D |
Measures temperature, humidity, pressure |
| Use Cases |
Compasses, orientation sensing |
Weather monitoring, indoor climate control, IoT |
| Key Features |
3-axis sensing, ultra-small, low power, low noise, I2C/SPI, 3.3V/5V |
3-in-1 sensor, high accuracy, low power, I2C/SPI, 3.3V/5V |
Features:
- Compact Form Factor: Ultra-small design for easy integration in space-constrained projects.
- Energy Efficiency: Low power consumption for prolonged operational hours.
- Precision and Reliability: Ultra-low noise guarantees accurate altitude measurements.
- Versatile Connectivity: Supports both I2C and SPI interfaces.
- Voltage Adaptability: Compatible with 3.3V and 5V systems.
Principle of Work
Internal Operation:
- Magnetometer Sensor Elements: Three sensor elements measure the magnetic field along X, Y, and Z axes using the Hall effect.
- Magnetic Field Measurement: Continuously measures strength and direction along all axes.
- Analog to Digital Conversion: Converts analog Hall effect signals into digital data.
- Data Processing: Calculates net magnetic field vector with error and temperature compensation.
- Output: Digital data available via I2C or SPI interfaces.
Interaction with MCU:
- Initialization: MCU sends setup commands via I2C or SPI.
- Data Retrieval: MCU reads magnetic field data along X, Y, Z axes.
- Data Processing: MCU calibrates and converts raw data, optionally fusing with accelerometer/gyroscope data.
- Algorithm Integration: Determine orientation or heading relative to Earth's magnetic field.
- Application-Specific Functions: Digital compass, drone navigation, augmented reality heading info, etc.
Module Pinout:

| Pin |
Description |
Additional Information |
| VCC |
Power input |
Provides voltage to the sensor. |
| GND |
Ground |
Electrical ground reference. |
| SDA |
I2C Data |
I2C data line. |
| SCL |
I2C Clock |
I2C clock line. |
| INT |
Interrupt Output |
Connect to I/O pin for event signaling. |
| SDO |
SPI Data Out (MISO) |
Data from sensor to host. |
| SDI |
SPI Data In (MOSI) |
Data from host to sensor. |
| CS |
Chip Selection |
Enable/disable sensor communication. |
| DRY |
Data Ready |
Signals when sensor is ready to send/receive data. |
Applications:
- Wearables: Altitude monitoring for fitness and outdoor tracking.
- Audible Devices: Elevation-based navigation or audio applications.
- Drones: Precise altitude measurements for stable flight.
- Altimeters: Accurate altitude readings for any device.
- Environmental Monitoring: Real-time data for research and studies.
- IoT Projects: Enhances IoT applications with critical altitude data.
Circuit Connection:

| Module Pin |
Arduino Uno Pin |
Description |
| VCC |
5V |
Power input connection. |
| GND |
GND |
Ground connection. |
| SDA |
SDA |
I2C data line. |
| SCL |
SCL |
I2C clock line. |
| INT |
NC |
No connection; optional interrupt usage. |
Library & Code:
Download the example demo and copy the Arduino folder into your code directory. The included sketch initializes the BMM150, reads magnetic data along X, Y, Z axes, and prints results to the serial monitor.
Technical Details:
- Operating voltage: 3.3V / 5V
- Communication interface: I2C / SPI
- Resolution: 0.3 μT
- Linearity: <1% FS
- Gain error: ±2%
- Temperature drift: ±0.01% / K
- Zero point drift: ±40 μT (25°C)
- Measuring range: ±1300 μT (X,Y), ±2500 μT (Z)
- Data output rate: 10 Hz (normal mode)
- Operating temperature: -40~85°C
- Dimensions: 29mm × 20mm
Comparisons:
| Aspect |
BMM150 |
BME280 |
| Type |
3-Axis Magnetometer |
Environmental Sensor (3-in-1) |
| Functionality |
Measures magnetic fields in 3D |
Measures temperature, humidity, pressure |
| Use Cases |
Compasses, orientation sensing |
Weather monitoring, indoor climate control, IoT |
| Key Features |
3-axis sensing, ultra-small, low power, low noise, I2C/SPI, 3.3V/5V |
3-in-1 sensor, high accuracy, low power, I2C/SPI, 3.3V/5V |


